Osgood schlatter Disease
What Is Osgood-Schlatter Disease?
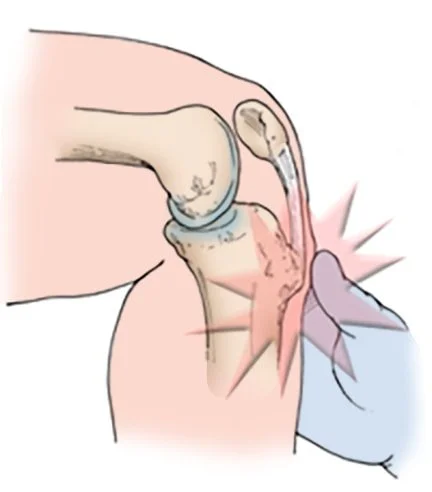
Osgood-Schlatter disease is swelling and irritation of the growth plate at the top of the shin one (tibial tuberosity) This is the site where the patella tendon attaches to. A growth plate is a layer of cartilage near the end of a bone where most of the bone's growth happens. It is weaker and more at risk for injury than the rest of the bone. Osgood- Schlatter Disease usually goes away when a child stops growing and usually doesn't cause lasting problems.
How is it diagnosed?
OSD typically causes pain and swelling below the kneecap.
The pain usually gets worse with running, jumping, going up stairs, and walking up hills.
Severe pain may lead to limping.
Osgood-Schlatter disease can happen in one or both knees.
How does it occur? Can it be prevented?
Osgood-Schlatter Disease is an overuse disease. It occurs due to quick growth where the muscles become excessively tight as the bones grow too quickly for the muscles to adapt to the change. This coupled with excessive/repetitive use leads to stress over the growth plate near the bone and pain as a result.
Prevention is tricky as growth is inconsistent between person to person. These strategies can help:
Regular foam rolling
Stretching and Strengtheing programs
Load and activity management
Regular measuring to pick up on growth spurts to be predictive in when this and other growth related disorders may occur.
Who is most affected?
Active Children during and after growth spurts. This is most common between 9-14 years old however either side of this can also happen.
How can Physiotherapy help?
Physiotherapy can help Osgood-Schlatter Disease by:
Correctly diagnosing and assessing of injury.
Providing advice on pain management (ice, foam rolling, taping)
Assessing dynamic postures and biomechanics
Advising on activity modification whilst symptomatic: this can include periods of rest when symptoms are irritable. Minimising excessive activity is also important.
Building an exercise program to address weakness, tightness and muscle imbalance.
Advice on appropriate footwear.
Planning return to activity if time off is required.
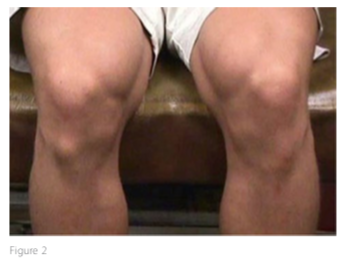
Visible bump from Bony changes caused by long standing Osgood-Schlatter disease.